Heating & Cooling

Energy Saving Guide

Heat & cool your home for less
Heating and cooling account for around a quarter of the energy used in the average home.
So what should your priorities be if you want to save money on energy while staying comfortable? Here’s how to ice your costs.Keeping your climate under control
We’ll unpack the actions that matter most when you are looking to keep a lid on energy bills from heating and cooling your home.
1. Insulate your home from high energy bills
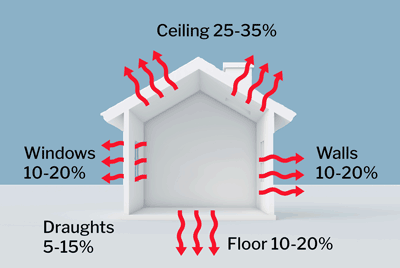
Heat loss and gain
Winter heat loss in a home with no insulation
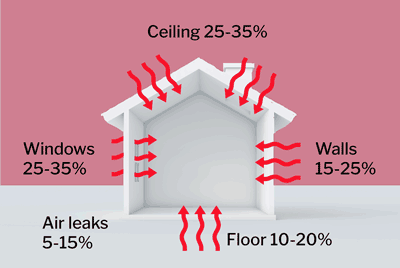
Summer heat gain in a home with no insulation
Source: yourhome.gov.au
- Ceilings
- Draughts and air leaks
- Walls
- Floors
- Windows
- Shading
Ceiling/Roof insulation
The roof is the area with the largest potential to absorb or lose heat. This can be fixed by installing the right amount of bulk insulation above the ceiling, including batts, blankets or loose fill. Reflective insulation placed under the roof will also help. Insulation is measured in R-Value – the bigger the number, the more effective. Bulk ceiling insulation is available in R-Values from 2.5 up to 7.0. Depending on your roof type, reflective insulation placed under the roof also adds another 1.0 R-Value. Reflective insulation is less effective at holding heat in a building. The values of two layers can be added together to determine the total R-Value.
How much roof insulation do I need?
How much you’ll need depends on where you live, the type and colour of your roof. Many Australian homes have medium or dark coloured roofs. This means they absorb the suns heat in a big way – a measure called absorptance. As a result you need more insulation the darker the roof. The Building Code of Australia recommends a minimum level of insulation. In reality, you’ll want to go more, because if even 2% of your ceiling is uninsulated they recommend you adds another 1R to compensate.
Minimum roof insulation by Australian climate zone
| Climate zone | Minimum Insulation R-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Roof colour (Absorptance level) | Roof colour is white or light grey (<0.4) | Roof is galvanised steel or zinc(0.4 to 0.6) | Roof colour is red or dark grey/black (>0.6) |
| Zone 1. Cairns. Darwin, Far North Queensland, NT, Nth WA | 3.1 | 4.1 | 5.1 |
| Zone 2-5. Sydney, Brisbane, Adelaide, Perth. Nth Vic, Central & Western NSW, Sth Queensland | 4.1 | 4.6 | 5.1 |
| Zone 6-7. Melbourne, Sth Vic, NSW Mountains | 4.6 | 5.1 | 5.1 |
| Zone 8. Alpine areas. Thredbo | 6.3 | 6.3 | 6.3 |
Draughts
In winter, draughts can account for up 25% of heat loss in some rooms. With some simple, cheap and effective fixes you can banish draughts. Here’s where to look for gaps and how to create a better seal.

Weather seals keep draughts out.
Downlights Halogen downlights come with a downside. That’s because they need space to stay cool so leave big gaps in ceiling insulation. To fix this replace halogen with capped LED downlights to seal off the airflow. Plus you’ll save on 80% on energy costs.

Wall insulation
About twenty percent of homes have wall insulation. If a house has timber framing and weatherboard or brick veneer, it’s possible to add insulation into the cavity through injection using bonded beads. The recommended minimum wall insulation is an R-Value of 2.8. Those are in alpine areas are advised to have R-Values above 3.8.
Floor insulation
If you have suspended timber flooring, there can be problems with airflow. Adding underfloor insulation can significantly reduce airflow into the home through the floor. A floor rug will also help insulate a room.
Rug up a room for warmth
Window insulation
Glass is amazing. Except when it comes to insulating a building. Single-glazed windows can transmit a huge amount of heat into and out of your home. In winter, up to 40% of heat can escape through windows – while in summer up to 80% of heat gained in room can be through glazing. If you live in a colder climate, then double glazing is the ultimate insulation. It is a substantial expense, but will provide appreciably better comfort, limit external noise and reduce annual energy bills. Framing in timber or uPVC offers superior insulation to aluminium windows. Cost effective fixes: Of course, there are things you can do to make a difference without installing new glazing. Window furnishing including well-fitted curtains or blinds assist insulation. In warmer locations, blinds on the outside are more effective in keeping heat out. You can also add window films to help tame the summer sun.
Fitted curtains will help cozy and cool your home
Throw some shade
Direct sun can generate serious heat in a home. Eaves, awnings and verandahs that shade the outside of homes can stop up to 90% of the sun’s heat. Aim to stop the high angled summer sun while inviting the low angle winter sun. Fixed shading options include;- Eaves or overhangs
- Fixed louvres
- Pergolas
- Shade sails
- Retractable awnings
- External blinds
- Adjustable louvres
- Shutters and screens

External blinds and shutters deliver summer shade.
The power of passive design
If you are building a new home or thinking about adding to your current home, it’s worth carefully considering how design can maximise your comfort. Passive house designs;- orientate the building and interior layout effectively
- shade the summer sun while inviting in the winter sun,
- capture cooling breezes,
- use building materials appropriate for the climate – high thermal mass in cold regions and lower thermal mass in hot regions
- maximise insulation.

Good building design will reduce energy costs for decades.
2. Cost effective heating and cooling
Heating Cost comparison
| Appliance | Running cost/per hour* |
|---|---|
| Small Room (16m2)** | |
| Reverse cycle air conditioner (3.5kW) (3.5 star) | 23c |
| Gas heater (3.2kW/13mJ) | 32c |
| Electric panel heater (2kW) | 49c |
| Medium Room (30m2)** | |
| Reverse cycle air conditioner (6kW) (3.5 star) | 44c |
| Gas heater (6.3kW/25mJ) | 62c |
| Electric panel heater or fan (4kW) | 99c |
| Whole House (160m2) | |
| Zoned ducted reverse cycle air conditioner | $1.10+ |
| Zoned ducted gas heater | $1.36+ |
| Non-zone ducted reverse cycle air conditioner | $1.47+ |
| Non-zoned ducted gas heater | $1.81+ |
Reverse cycle economics
Reverse cycle air conditioners can heat a room cheaper than the cost of the most efficient gas heater. Economic analysis commissioned by Energy Consumers Australia in the 2018 ATA Household Fuel Choice study found that if their gas heater fails, it is cheaper for homes to replace it with an efficient electric reverse cycle air conditioner. If homes have an existing reverse cycle air conditioner which is relatively efficient, the analysis determined it cheaper to ditch gas. For running costs and economics on gas, solar and electric water heating fuel – see the Hot Water Energy Saving Guide. Households with rooftop solar are even better candidates to sidestep gas heating.
Cooling Cost comparison
| Appliance | Running cost/per hour* |
|---|---|
| Portable and Ceiling Fans | Less than 5c |
| Portable evaporative cooler | Less than 7c |
| Portable air conditioner | 50c |
| Split air conditioner | |
| 2.5kW (3.5 star) (16m2 room) | 18c |
| 5.0kW (3.5 star) (30m2 room) | 37c |
| 7.1kW (3.0 star) (60m2 room) | 67c |
| Ducted air condition system (160m2 home) | $2.00+ |
3. Air conditioning essentials
Australia is a hot country. To be comfortable, many households need air conditioning. Here’s how you can maintain a high comfort level while keeping running costs low.
Get the temperature right
Changing the thermostat by just one degree can raise running costs by up to 10%. While the difference in air temperature is tiny, every degree requires a whole lot more energy. By adjusting your thermostat with the seasons you’ll still be comfortable while ensuring your air conditioner is efficient. Setting your thermostat between 24–27°C in summer will keep you cool. A setting of 18-20°C in winter will keep you warm.
Only heat or cool the space you need
You’ll be saving energy and money by only heating or cooling the rooms you are using. Zoned systems allow you to control where air conditioning is need avoid waste. By closing door and windows you’ll keep the temperature you need with less effort for the A/C unit. Don’t forget to take advantage of natural ventilation like summer breezes or the winter suns warmth to reduce the need to run appliances.
Run when energy is cheap
Take advantage of off-peak energy. Low cost off peak electricity is ideal to warm your house in the early morning so it’s comfortable when you wake up. This way you avoid more expensive tariffs during the day. Got solar? Use the electricity you generate guilt-free to power your air conditioner. Your PV system is at capacity during the heat of the day so you should use it. Program the timer on your air conditioner to cool the house in summer or warm in winter during the day. This ensures you’ll return to an inviting home which should last into the evening, reducing the need to buy electricity when prices are high.
Keep your A/C in good repair
Efficiency can fall by almost a third when an air conditioning unit is not well maintained. So think about servicing in line with the manufacturer’s recommended schedule using a qualified technician. If you have a unit that a decade or older, you may consider an upgrade. That’s because new systems can be up to 30% more energy efficient than older appliances.
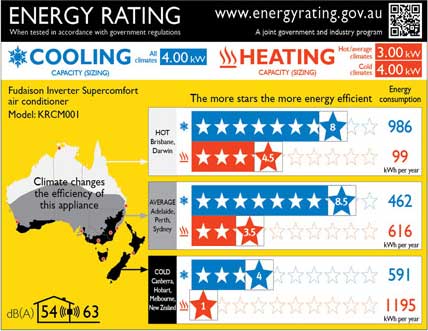
Buy smarter
Shopping for an energy-efficient appliance can offer long term savings that outweigh a higher upfront cost. You can now check energy ratings by region to compare the efficiency of air conditioners through www.energyrating.gov.au. Even better you’ll find the famous Energy ratings label has been updated to show efficiency by season for three distinct climate zones. More stars means lower running costs. Every added star can reduce running cost by 10%. There are two other thing to keep in mind when shopping for air conditions; Size matters: It’s important to match your system to your space. If it’s under or overpowered for the area, it won’t be as efficient. Do you need to be Demand ready?: If you live in Queensland, regulation requires that only air conditioners installed with DRED technology (Demand Response Enabled Device) can be fitted. This technology ensures that your power stays on exceptionally hot days. In other areas if you choose an air conditioner with a demand response capability, you may be able to benefit from incentives offered to owners. Agreeing to participate in Demand Response programs that turn down the appliance through the network when the grid is pushed to the limit, may provide rewards to owners.